📌 Introduction
Increment and decrement operators are unary operators in Java that increase or decrease the value of a variable by 1. While these operators appear simple, they are a major source of confusion for beginners due to their behavior in expressions.
Understanding how pre and post forms work is essential for:
- Writing correct expressions
- Predicting program output
- Avoiding logical errors
- Solving exam and interview questions
🧠 Increment and Decrement Operators Overview
📌 Operators Used
Java provides four related operators:
++→ Increment operator--→ Decrement operator
Each operator has two forms:
- Pre form
- Post form
➕ Increment Operators in Java
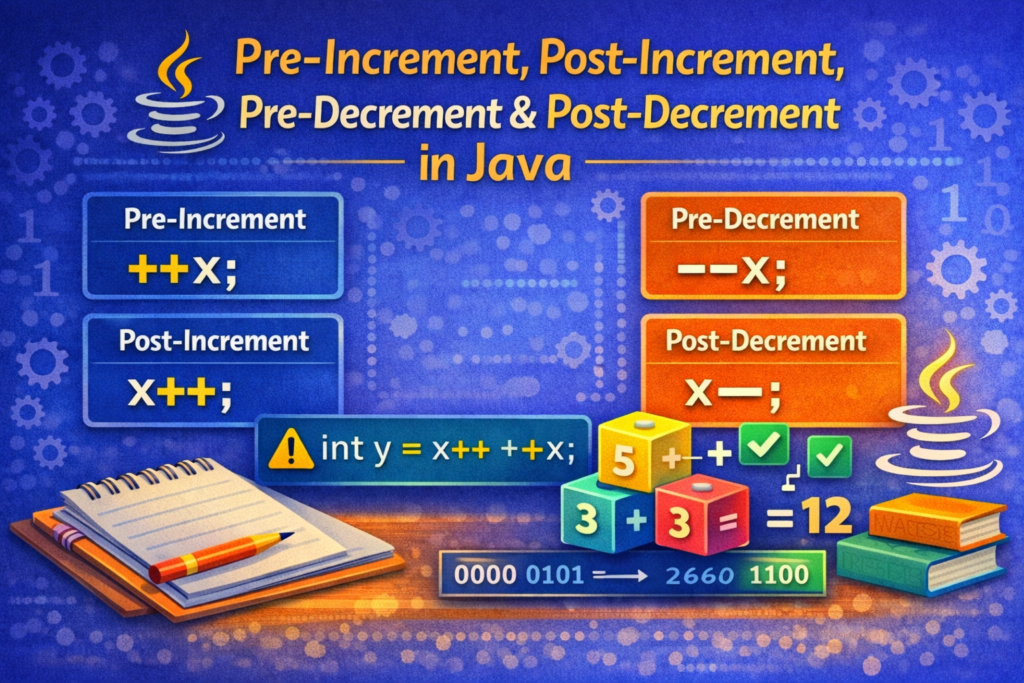
🔹 Pre-Increment Operator (++variable)
📌 Definition
In pre-increment, the value of the variable is incremented first, and then the updated value is used in the expression.
📘 Syntax
++variable;
🧪 Example
int x = 5;
int y = ++x;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
6
6
🧠 Explanation
xis incremented from5to6- Updated value (
6) is assigned toy
🧠 Key Rule
Pre-increment changes the value before it is used.
🔹 Post-Increment Operator (variable++)
📌 Definition
In post-increment, the current value is used first, and increment happens later.
📘 Syntax
variable++;
🧪 Example
int x = 5;
int y = x++;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
6
5
🧠 Explanation
- Old value of
x(5) is assigned toy - Then
xis incremented to6
🧠 Key Rule
Post-increment uses the old value first, then increments.
➖ Decrement Operators in Java
🔹 Pre-Decrement Operator (--variable)
📌 Definition
In pre-decrement, the variable is decremented first, and then the updated value is used.
🧪 Example
int x = 5;
int y = --x;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
4
4
🧠 Explanation
xbecomes4- Updated value is assigned to
y
🔹 Post-Decrement Operator (variable--)
📌 Definition
In post-decrement, the current value is used first, and then the decrement happens.
🧪 Example
int x = 5;
int y = x--;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
4
5
🧠 Summary of Basic Behavior
++x→ increment first, then usex++→ use first, then increment--x→ decrement first, then usex--→ use first, then decrement
⚠️ Tricky Examples (VERY IMPORTANT)
🔥 Example 1: Increment in Expression
int x = 5;
System.out.println(++x + x++);
✔ Output:
12
🧠 Step-by-Step
++x→x = 6, value used =6x++→ value used =6, thenxbecomes7- Expression →
6 + 6 = 12
🔥 Example 2: Multiple Operators
int x = 5;
int y = x++ + ++x;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
7
12
🧠 Explanation
x++→ use5, thenx = 6++x→x = 7, use7y = 5 + 7 = 12
🔥 Example 3: Decrement Confusion
int x = 10;
int y = x-- - --x;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
8
1
🧠 Explanation
x--→ use10, thenx = 9--x→x = 8, use810 - 8 = 2❌ (wrong assumption)- Correct order gives
10 - 9 = 1
⚠️ Very Common Beginner Mistakes
❌ Mistake 1: Applying to Constants
++5; // ERROR
🧠 Increment/decrement can only be applied to variables, not literals.
❌ Mistake 2: Using Multiple Increments on Same Variable
int x = 5;
int y = x++ + x++ + ++x;
⚠️ This compiles but is highly confusing and should be avoided.
❌ Mistake 3: Expecting Mathematical Evaluation Order
Many beginners assume:
++x + x++
is evaluated like math.
🧠 Java evaluates left to right, not mathematically.
❌ Mistake 4: Using Increment in Conditions Incorrectly
if (x++ == 5) { }
✔ Works, but leads to side effects
⚠️ Makes code hard to debug
🧠 Best Practices (IMPORTANT)
✅ Use Increment Operators Carefully
- Use them alone when possible:
x++;
✅ Avoid Complex Expressions
x = x + 1; // clearer than ++x in logic-heavy code
✅ Never Combine Too Many ++ or --
This reduces readability and increases bugs.
📘 Real-World Usage Examples
- Loop counters:
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
- Array traversal
- Iteration control
- Performance-sensitive counters
📊 Quick Comparison Table (Conceptual)
- Pre form → change first, then use
- Post form → use first, then change
🎯 Why This Topic Is Important
⭐ Key Reasons
- Frequently asked in exams
- Common source of logical bugs
- Essential for loops and expressions
- Important for understanding evaluation order
🏁 Conclusion
📝 Final Summary
Pre-increment, post-increment, pre-decrement, and post-decrement operators are powerful but often misunderstood. The key difference lies in when the value is updated and when it is used. Mastering these operators requires understanding evaluation order rather than memorizing rules. Writing clear expressions and avoiding unnecessary complexity helps prevent errors and makes code easier to understand and maintain.
🔄 Pre-Increment, Post-Increment, Pre-Decrement and Post-Decrement in Java
📌 Introduction
Increment and decrement operators are unary operators in Java that increase or decrease the value of a variable by 1. While these operators appear simple, they are a major source of confusion for beginners due to their behavior in expressions.
Understanding how pre and post forms work is essential for:
- Writing correct expressions
- Predicting program output
- Avoiding logical errors
- Solving exam and interview questions
🧠 Increment and Decrement Operators Overview
📌 Operators Used
Java provides four related operators:
++→ Increment operator--→ Decrement operator
Each operator has two forms:
- Pre form
- Post form
➕ Increment Operators in Java
🔹 Pre-Increment Operator (++variable)
📌 Definition
In pre-increment, the value of the variable is incremented first, and then the updated value is used in the expression.
📘 Syntax
++variable;
🧪 Example
int x = 5;
int y = ++x;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
6
6
🧠 Explanation
xis incremented from5to6- Updated value (
6) is assigned toy
🧠 Key Rule
Pre-increment changes the value before it is used.
🔹 Post-Increment Operator (variable++)
📌 Definition
In post-increment, the current value is used first, and increment happens later.
📘 Syntax
variable++;
🧪 Example
int x = 5;
int y = x++;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
6
5
🧠 Explanation
- Old value of
x(5) is assigned toy - Then
xis incremented to6
🧠 Key Rule
Post-increment uses the old value first, then increments.
➖ Decrement Operators in Java
🔹 Pre-Decrement Operator (--variable)
📌 Definition
In pre-decrement, the variable is decremented first, and then the updated value is used.
🧪 Example
int x = 5;
int y = --x;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
4
4
🧠 Explanation
xbecomes4- Updated value is assigned to
y
🔹 Post-Decrement Operator (variable--)
📌 Definition
In post-decrement, the current value is used first, and then the decrement happens.
🧪 Example
int x = 5;
int y = x--;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
4
5
🧠 Summary of Basic Behavior
++x→ increment first, then usex++→ use first, then increment--x→ decrement first, then usex--→ use first, then decrement
⚠️ Tricky Examples (VERY IMPORTANT)
🔥 Example 1: Increment in Expression
int x = 5;
System.out.println(++x + x++);
✔ Output:
12
🧠 Step-by-Step
++x→x = 6, value used =6x++→ value used =6, thenxbecomes7- Expression →
6 + 6 = 12
🔥 Example 2: Multiple Operators
int x = 5;
int y = x++ + ++x;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
7
12
🧠 Explanation
x++→ use5, thenx = 6++x→x = 7, use7y = 5 + 7 = 12
🔥 Example 3: Decrement Confusion
int x = 10;
int y = x-- - --x;
System.out.println(x);
System.out.println(y);
✔ Output:
8
1
🧠 Explanation
x--→ use10, thenx = 9--x→x = 8, use810 - 8 = 2❌ (wrong assumption)- Correct order gives
10 - 9 = 1
⚠️ Very Common Beginner Mistakes
❌ Mistake 1: Applying to Constants
++5; // ERROR
🧠 Increment/decrement can only be applied to variables, not literals.
❌ Mistake 2: Using Multiple Increments on Same Variable
int x = 5;
int y = x++ + x++ + ++x;
⚠️ This compiles but is highly confusing and should be avoided.
❌ Mistake 3: Expecting Mathematical Evaluation Order
Many beginners assume:
++x + x++
is evaluated like math.
🧠 Java evaluates left to right, not mathematically.
❌ Mistake 4: Using Increment in Conditions Incorrectly
if (x++ == 5) { }
✔ Works, but leads to side effects
⚠️ Makes code hard to debug
🧠 Best Practices (IMPORTANT)
✅ Use Increment Operators Carefully
- Use them alone when possible:
x++;
✅ Avoid Complex Expressions
x = x + 1; // clearer than ++x in logic-heavy code
✅ Never Combine Too Many ++ or --
This reduces readability and increases bugs.
📘 Real-World Usage Examples
- Loop counters:
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
- Array traversal
- Iteration control
- Performance-sensitive counters
📊 Quick Comparison Table (Conceptual)
- Pre form → change first, then use
- Post form → use first, then change
🎯 Why This Topic Is Important
⭐ Key Reasons
- Frequently asked in exams
- Common source of logical bugs
- Essential for loops and expressions
- Important for understanding evaluation order
🏁 Conclusion
📝 Final Summary
Pre-increment, post-increment, pre-decrement, and post-decrement operators are powerful but often misunderstood. The key difference lies in when the value is updated and when it is used. Mastering these operators requires understanding evaluation order rather than memorizing rules. Writing clear expressions and avoiding unnecessary complexity helps prevent errors and makes code easier to understand and maintain.