⌨️ Accepting User Input in Java Using Scanner Class
📌 Introduction
Most real-world programs are interactive, meaning they need to accept input from the user at runtime. Java provides several ways to take input, and among them, the Scanner class is the most commonly used and beginner-friendly approach.
The Scanner class allows programs to read different types of data such as integers, floating-point numbers, characters, and strings from standard input (keyboard).
🧠 Why Do We Need User Input?
📌 Importance of Input
Without user input, programs become static and inflexible. Accepting input allows:
- Dynamic execution
- User interaction
- Reusability of programs
- Real-world problem solving
Example:
- Taking marks from a student
- Reading numbers for calculations
- Accepting usernames and passwords
📦 What Is the Scanner Class?
📌 Definition
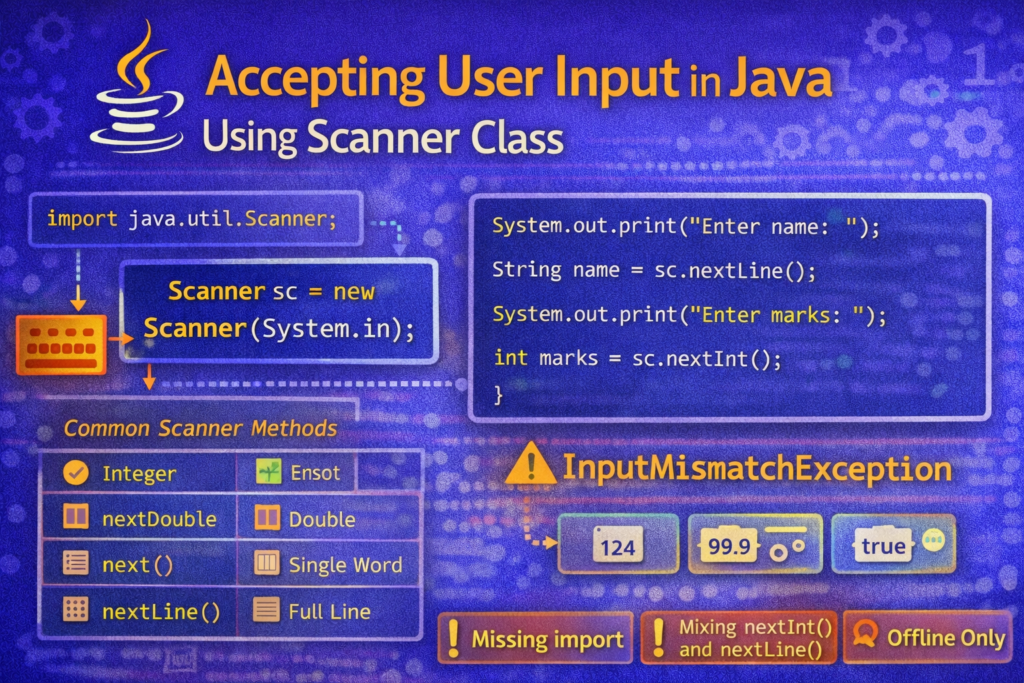
The Scanner class is a predefined class present in the java.util package. It is used to read input from various sources, most commonly keyboard input via System.in.
📥 Importing the Scanner Class
📌 Mandatory Step
Before using Scanner, it must be imported.
import java.util.Scanner;
❌ If not imported:
Scanner cannot be resolved to a type
🛠️ Creating a Scanner Object
📌 Syntax
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
🧠 Explanation
Scanner→ class namesc→ reference variableSystem.in→ standard input stream (keyboard)
🧪 Example: Reading an Integer
import java.util.Scanner;
class InputDemo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
int number = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("You entered: " + number);
sc.close();
}
}
📚 Commonly Used Scanner Methods
📌 Important Methods
| Method | Description |
|---|---|
nextInt() | Reads integer |
nextFloat() | Reads float |
nextDouble() | Reads double |
next() | Reads single word |
nextLine() | Reads full line |
nextBoolean() | Reads boolean |
🧠 Reading Different Data Types
🔹 Reading a String (Single Word)
String name = sc.next();
✔ Reads input until space is encountered.
🔹 Reading a Full Line
String sentence = sc.nextLine();
✔ Reads entire line including spaces.
🔥 Very Common Confusion: next() vs nextLine()
| Method | Reads |
|---|---|
next() | One word |
nextLine() | Full line |
⚠️ Most Common Scanner Confusion (VERY IMPORTANT)
❌ Mixing nextInt() and nextLine()
int age = sc.nextInt();
String name = sc.nextLine(); // Problem
🧠 nextInt() leaves a newline character in the buffer, which nextLine() immediately consumes.
✅ Correct Way (Solution)
int age = sc.nextInt();
sc.nextLine(); // consume leftover newline
String name = sc.nextLine();
⚠️ Common Compilation & Runtime Errors
❌ Error 1: Missing Import
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
✔ Fix:
import java.util.Scanner;
❌ Error 2: Scanner Not Closed
Not closing Scanner can cause resource leak warnings.
✔ Best Practice:
sc.close();
❌ Error 3: InputMismatchException
int x = sc.nextInt(); // user enters string
✔ Runtime Exception:
InputMismatchException
🧠 Input type must match method.
🔥 Tricky Example 1: Character Input
Scanner does not have nextChar().
❌ Invalid:
char ch = sc.nextChar();
✔ Correct:
char ch = sc.next().charAt(0);
🔥 Tricky Example 2: Boolean Input
boolean status = sc.nextBoolean();
✔ Accepts only:
true or false
❌ Invalid:
yes / no
⚠️ Important Note About Online Compilers (VERY IMPORTANT)
📌 Scanner Limitation
The Scanner class works only in environments that provide real keyboard input, such as:
- Command Prompt
- Terminal
- IDEs (Eclipse, IntelliJ, VS Code)
❌ Many online or embedded compilers do not support System.in, causing Scanner programs to fail or hang.
👉 In such cases, offline execution is required.
🧠 Best Practices While Using Scanner
✔ Import Correct Package
Always import java.util.Scanner.
✔ Use Correct Method for Data Type
Match input type with method.
✔ Avoid Mixing Methods Without Care
Handle newline issues properly.
✔ Close Scanner After Use
Releases system resources.
📘 Real-World Example: Student Input Program
Scanner sc = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.print("Enter name: ");
String name = sc.nextLine();
System.out.print("Enter marks: ");
int marks = sc.nextInt();
System.out.println("Name: " + name);
System.out.println("Marks: " + marks);
sc.close();
📌 Quick Summary
Scanneris used for runtime input- Belongs to
java.utilpackage - Uses
System.infor keyboard input - Different methods for different data types
- Mixing input methods requires care
- Works best in offline environments
🏁 Conclusion
The Scanner class is an essential tool for writing interactive Java programs. While it is easy to use, beginners often face confusion due to method behavior, input mismatches, and environment limitations. Understanding how Scanner works internally, choosing the correct input methods, and following best practices ensures reliable and error-free programs.