🧠 Logical Operators in Java
📌 Introduction
Logical operators in Java are used to combine multiple conditions and produce a single boolean result (true or false). They are extensively used in:
ifandelsestatements- loops
- complex decision-making logic
Logical operators work only on boolean expressions and are typically used along with relational operators.
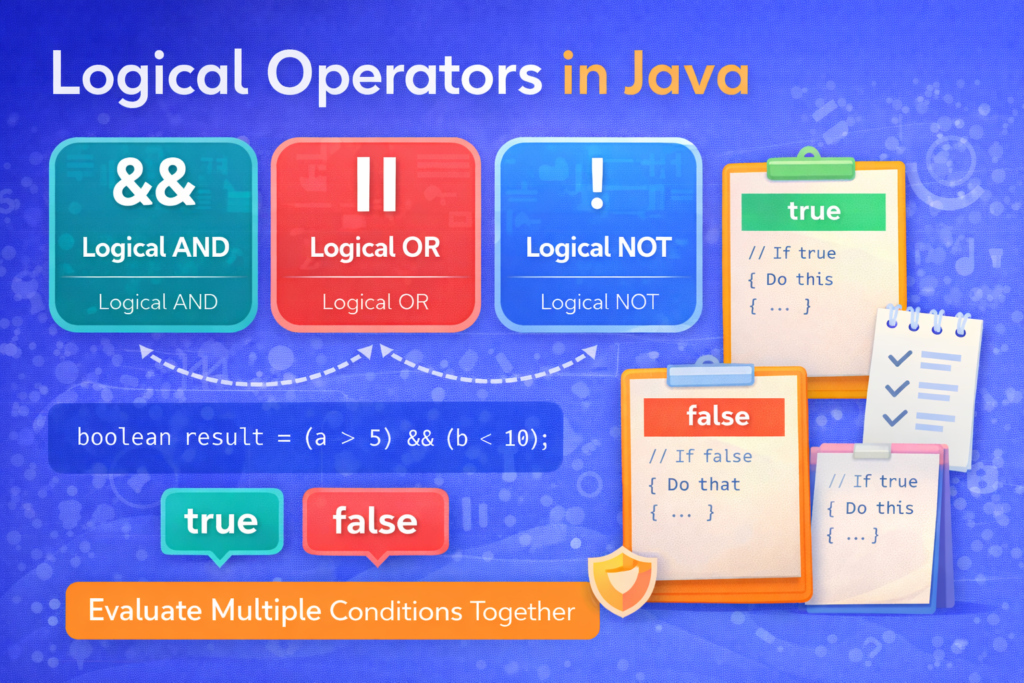
🧩 What Are Logical Operators?
📘 Definition
Logical operators evaluate one or more boolean expressions and return a boolean result.
✔ Result is always:
true or false
📊 List of Logical Operators in Java
| Operator | Name | Description |
|---|---|---|
&& | Logical AND | True if both conditions are true |
|| | Logical OR | True if at least one condition is true |
! | Logical NOT | Reverses the condition |
🔗 1. Logical AND Operator (&&)
📌 Basic Meaning
The AND operator returns true only if both conditions are true.
int a = 10;
int b = 5;
System.out.println(a > 5 && b < 10);
✔ Output:
true
📊 Truth Table for AND (&&)
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| true | true | true |
| true | false | false |
| false | true | false |
| false | false | false |
⚠️ Common Confusion
System.out.println(10 > 5 && 5 > 20);
✔ Output:
false
🧠 Both conditions must be true.
🔥 Short-Circuit Behavior (VERY IMPORTANT)
int x = 10;
System.out.println(x > 20 && ++x > 10);
System.out.println(x);
✔ Output:
false
10
🧠 Explanation:
- First condition is false
- Java does NOT evaluate the second condition
++xnever executes
❌ Common Mistake
Assuming both conditions always execute.
🔀 2. Logical OR Operator (||)
📌 Basic Meaning
The OR operator returns true if at least one condition is true.
int age = 17;
System.out.println(age < 18 || age > 60);
✔ Output:
true
📊 Truth Table for OR (||)
| Condition 1 | Condition 2 | Result |
|---|---|---|
| true | true | true |
| true | false | true |
| false | true | true |
| false | false | false |
🔥 Short-Circuit Behavior (IMPORTANT)
int x = 10;
System.out.println(x < 20 || ++x > 10);
System.out.println(x);
✔ Output:
true
10
🧠 Explanation:
- First condition is true
- Java skips second condition
xis not incremented
⚠️ Tricky Example
System.out.println(false || false || true);
✔ Output:
true
🔄 Difference Between && and & (CRITICAL CONFUSION)
📌 Introduction
In Java, both && and & can be used with boolean expressions, which often leads to confusion among beginners. Although they may sometimes produce the same output, their behavior during condition evaluation is very different.
Understanding this difference is extremely important to avoid:
- Unexpected variable changes
- Logical bugs
- Performance issues in conditional statements
🧠 Nature of the Operators
The operator && is called the logical AND operator, whereas & is primarily a bitwise AND operator that can also work with boolean values.
When used in conditions:
&&is a short-circuit logical operator&is a non short-circuit operator
This distinction directly affects how Java evaluates expressions.
🔁 Evaluation of Conditions
When the && operator is used, Java evaluates the left-hand condition first.
If the first condition evaluates to false, Java does not evaluate the second condition, because the final result is guaranteed to be false.
In contrast, when the & operator is used, both conditions are always evaluated, regardless of the result of the first condition.
🧪 Example Using && (Short-Circuit AND)
int x = 10;
System.out.println(x < 5 && ++x > 10);
System.out.println(x);
✔ Output:
false
10
🧠 Explanation:
x < 5isfalse- Java skips the second condition
++xdoes not execute- Value of
xremains unchanged
This makes && safe and efficient for conditional checks.
🧪 Example Using & (Non Short-Circuit AND)
int x = 10;
System.out.println(x < 5 & ++x > 10);
System.out.println(x);
✔ Output:
false
11
🧠 Explanation:
- Both conditions are evaluated
++xexecutes even though the first condition is falsexis incremented unintentionally
This can cause side effects, especially when increment operators or method calls are involved.
⚠️ Performance Consideration
The && operator avoids unnecessary evaluation of conditions, which:
- Improves performance
- Prevents unwanted execution
- Reduces logical errors
The & operator always evaluates both expressions, which can:
- Slow down execution
- Cause unexpected changes in variable values
⚠️ Common Beginner Mistake
A frequent mistake is using & instead of && in if statements. While the program may compile and sometimes even produce correct output, it can fail in real-world scenarios due to unwanted execution of the second condition.
✅ Correct Usage Recommendation
- Use
&&in:ifconditions- loops
- validations
- decision-making logic
- Use
&only when:- You intentionally want both conditions to be evaluated
- You are performing bitwise operations
🎯 Key Takeaway
Even though && and & may look similar, they serve different purposes. The logical AND operator && is designed for safe, efficient conditional evaluation, while & always evaluates both expressions and should be used cautiously.
For logical conditions and control flow, && is always the correct and recommended choice.
🔄 Difference Between || and |
📌 Introduction
In Java, both || and | can be used with boolean expressions, which often creates confusion among beginners. Although they look similar and may sometimes produce the same result, their behavior is fundamentally different, especially in how they evaluate conditions.
Understanding this difference is crucial to avoid logical bugs, unexpected side effects, and performance issues.
🧠 Nature of the Operators
The operator || is known as the logical OR operator, whereas | is primarily a bitwise OR operator that can also work with boolean values.
When used in conditions:
||is a short-circuit logical operator|is a non short-circuit operator
This single difference changes how Java evaluates expressions.
🔁 Evaluation of Conditions
When the || operator is used, Java evaluates the left-hand condition first.
If that condition evaluates to true, Java does not evaluate the right-hand condition at all, because the final result is already known to be true.
On the other hand, when the | operator is used, both conditions are always evaluated, regardless of the result of the first condition.
🧪 Example Using || (Short-Circuit OR)
int x = 10;
System.out.println(x > 5 || ++x > 10);
System.out.println(x);
✔ Output:
true
10
🧠 Explanation:
x > 5istrue- Java skips the second condition
++xis never executed- Value of
xremains unchanged
This behavior makes || safe and efficient for conditional checks.
🧪 Example Using | (Non Short-Circuit OR)
int x = 10;
System.out.println(x > 5 | ++x > 10);
System.out.println(x);
✔ Output:
true
11
🧠 Explanation:
- Both conditions are evaluated
++xexecutes even though first condition istrue- Value of
xchanges unexpectedly
This can introduce side effects, especially when method calls or increment operations are involved.
⚠️ Performance Consideration
Because || skips unnecessary condition evaluation, it is:
- Faster
- More optimized
- Preferred in conditional logic
The | operator always evaluates both sides, which can:
- Reduce performance
- Cause unintended execution of code
⚠️ Common Beginner Mistake
Many beginners accidentally use | instead of || in if conditions, assuming both behave the same. While the output may look correct initially, the program can behave incorrectly in complex conditions due to unintended execution of the second expression.
✅ Correct Usage Recommendation
- Use
||in:ifstatements- loops
- validations
- decision-making logic
- Use
|only when:- You explicitly want both expressions to be evaluated
- You are performing bitwise operations
🎯 Key Takeaway
Although || and | may appear similar, they serve different purposes. The logical OR operator || is designed for safe and efficient conditional evaluation, while | evaluates all conditions and should be used cautiously.
For logical conditions and control flow, || is always the correct and recommended choice.
🔁 3. Logical NOT Operator (!)
📌 Basic Meaning
Logical NOT reverses the result of a condition.
boolean isJavaEasy = false;
System.out.println(!isJavaEasy);
✔ Output:
true
⚠️ Common Confusion
System.out.println(!(10 > 5));
✔ Output:
false
🧠 NOT applies to the entire condition inside parentheses.
❌ Wrong Usage
System.out.println(!10 > 5); // ERROR
❌ Compilation Error
🧠 ! works only on boolean expressions.
⚠️ Common Mistakes with Logical Operators
❌ 1. Using logical operators with non-boolean values
System.out.println(10 && 20); // ERROR
❌ 2. Confusing && with &
Leads to unexpected side effects.
❌ 3. Forgetting Parentheses
if (a > b && c > d || e > f)
🧠 Hard to read and error-prone.
✔ Better:
if ((a > b && c > d) || e > f)
❌ 4. Assuming Both Conditions Execute
Short-circuit operators skip evaluation.
🧠 Operator Precedence Reminder
📌 Evaluation Order
- Arithmetic operators
- Relational operators
- Logical operators
System.out.println(10 + 5 > 12 && 8 > 3);
✔ Output:
true
📊 Summary Table
| Operator | Name | Short-Circuit |
|---|---|---|
&& | Logical AND | Yes |
| ` | ` | |
! | Logical NOT | Not applicable |
& | AND | No |
| ` | ` | OR |
🎯 Why Logical Operators Are Important
⭐ Key Importance
- Enable complex conditions
- Control program flow
- Used in loops and validations
- Essential for decision-making logic
🏁 Conclusion
📝 Final Summary
Logical operators allow Java programs to evaluate multiple conditions efficiently. Understanding short-circuit behavior, correct operator usage, and common pitfalls is crucial for writing correct and optimized code.
A strong grasp of logical operators prepares learners for control statements, where conditions play a central role.