📌 Introduction
In Java, data types specify the type of data a variable can store. They play a crucial role in:
- Memory allocation
- Data representation
- Program efficiency
- Error prevention
Before storing any value in a variable, Java must know what kind of data it is.
🧠 Types of Data Types in Java
📂 Classification of Data Types
Java data types are broadly classified into two categories:
- Primitive Data Types
- Non-Primitive Data Types
📌 Primitive vs Non-Primitive
- Primitive data types store simple values directly
- Non-primitive data types store references to objects
👉 In this article, we will focus only on Primitive Data Types.
🧱 What Are Primitive Data Types?
📘 Definition
Primitive data types are the basic building blocks of data in Java. They store simple values and are not objects.
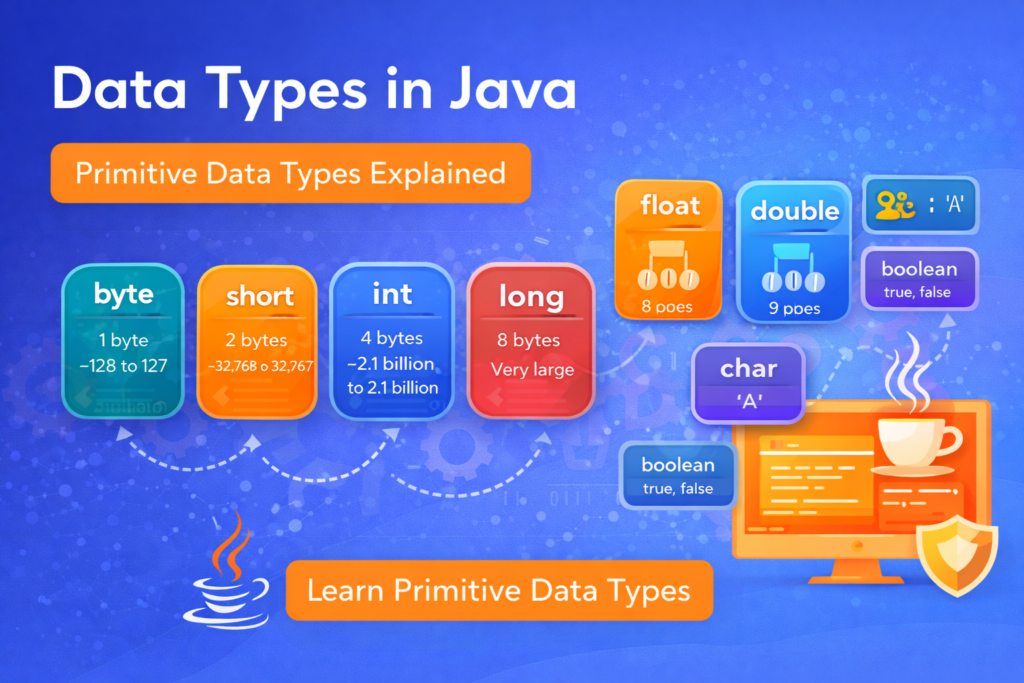
Java has 8 primitive data types, divided into logical groups.
📊 Classification of Primitive Data Types
| Category | Data Types |
|---|---|
| Integer | byte, short, int, long |
| Floating-Point | float, double |
| Character | char |
| Boolean | boolean |
🔢 Integer Data Types (MOST IMPORTANT)
Integer data types are used to store whole numbers (positive, negative, and zero).
🔹 byte Data Type
📌 Overview
- Size: 1 byte (8 bits)
- Range: –128 to +127
- Default value:
0
byte b = 10;
🧠 Why Is byte Range –128 to +127?
This is one of the most important concepts in Java and computer science.
Let’s understand this slowly and clearly.
📦 How Data Is Stored in Memory
Computers store data in binary format (0s and 1s).
- 1 bit → can store 0 or 1
- 8 bits → can store 2⁸ = 256 values
Since byte uses 8 bits, it can represent 256 different values.
⚖️ Why Both Positive and Negative Numbers?
Java uses signed integers, meaning:
- Some values are reserved for negative numbers
- Some for positive numbers
- One for zero
This is achieved using a system called Two’s Complement.
🔁 Two’s Complement (CRITICAL CONCEPT)
📌 What Is Two’s Complement?
Two’s complement is a method used to represent negative numbers in binary.
Java uses two’s complement for all integer data types.
🧮 Binary Representation of byte
A byte has 8 bits:
b7 b6 b5 b4 b3 b2 b1 b0
- The leftmost bit (b7) is the sign bit
0→ positive number1→ negative number
📊 Range Calculation
- Total combinations = 256
- Half used for negative numbers
- Half used for non-negative numbers
So the range becomes:
-2⁷ to +2⁷ – 1
= -128 to +127
🧪 Example: Storing +5 in byte
Binary of 5:
00000101
Sign bit = 0 → positive number
🧪 Example: Storing –5 in byte (Two’s Complement)
Steps:
- Binary of +5 →
00000101 - 1’s complement →
11111010 - Add 1 →
11111011
This binary now represents –5.
🔑 Key Takeaway
- Two’s complement allows easy arithmetic
- Zero has only one representation
- Most efficient for hardware operations
🔹 short Data Type
📌 Overview
- Size: 2 bytes (16 bits)
- Range: –32,768 to +32,767
- Default value:
0
short s = 2000;
🧠 Why This Range?
- 16 bits → 2¹⁶ = 65,536 values
- Two’s complement system
- Range becomes:
-2¹⁵ to +2¹⁵ – 1
🔹 int Data Type (MOST COMMONLY USED)
📌 Overview
- Size: 4 bytes (32 bits)
- Range: –2,147,483,648 to +2,147,483,647
- Default value:
0
int number = 100000;
📌 Why int Is Default?
Java uses int by default because:
- Balanced memory usage
- Fast performance
- Suitable for most calculations
🔹 long Data Type
📌 Overview
- Size: 8 bytes (64 bits)
- Range: Very large
- Suffix:
L
long population = 7800000000L;
🔢 Floating-Point Data Types
Used to store decimal values.
🔹 float Data Type
📌 Overview
- Size: 4 bytes
- Precision: ~7 decimal digits
- Suffix:
f
float pi = 3.14f;
🔹 double Data Type
📌 Overview
- Size: 8 bytes
- Precision: ~15 decimal digits
- Default floating-point type
double value = 3.1415926535;
🔤 Character Data Type
🔹 char Data Type
📌 Overview
- Size: 2 bytes
- Stores a single character
- Uses Unicode
char grade = 'A';
🧠 Why 2 Bytes?
Java supports international characters, so it uses Unicode instead of ASCII.
🔘 Boolean Data Type
🔹 boolean Data Type
📌 Overview
- Values:
trueorfalse - Size: JVM-dependent (logical)
boolean isJavaFun = true;
📊 Summary Table: Primitive Data Types
| Data Type | Size | Range |
|---|---|---|
| byte | 1 byte | –128 to 127 |
| short | 2 bytes | –32,768 to 32,767 |
| int | 4 bytes | –2.1 billion to 2.1 billion |
| long | 8 bytes | Very large |
| float | 4 bytes | Decimal (7 digits) |
| double | 8 bytes | Decimal (15 digits) |
| char | 2 bytes | Unicode characters |
| boolean | JVM dependent | true / false |
🎯 Why Understanding Primitive Data Types Is Important
⭐ Key Reasons
- Efficient memory usage
- Prevents overflow errors
- Improves performance
- Essential for low-level understanding
- Frequently asked in exams and interviews
🏁 Conclusion
📝 Final Summary
Primitive data types form the foundation of Java programming. Understanding how data is stored, especially integer representation using two’s complement, helps in writing efficient, correct, and optimized programs.
A strong grasp of primitive data types is essential before moving to:
- Operators
- Control statements
- Arrays
- Object-oriented concepts